Corporate carbon footprint: What it is and why it matters.
A corporate carbon footprint refers to the total amount of greenhouse gases, expressed as carbon dioxide equivalent, produced directly and indirectly by a company. This encompasses the entire scope of a company’s activities and the impact of its products, including but not limited to manufacturing, transportation, energy use, and waste disposal. Assessing and addressing corporate carbon footprints has become increasingly important in the context of climate change and sustainability.
By quantifying their carbon footprint, businesses can identify opportunities to reduce their environmental impact and mitigate climate change. This may involve implementing energy-efficient technologies, optimizing transportation and logistics, sourcing renewable energy, and implementing waste reduction strategies. Additionally, many organizations use carbon offsetting initiatives to compensate for their unavoidable emissions by investing in environmental projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions elsewhere.
Measuring and managing a corporate carbon footprint not only contributes to environmental sustainability but can also yield cost savings, enhance brand reputation, and attract environmentally conscious consumers and investors. As such, many companies are incorporating carbon footprint reduction strategies into their overall corporate sustainability efforts.
Utility data is the key to reducing corporate carbon footprint.
Data from utility providers is essential, but it is also the backbone of determining the corporate carbon footprint. It provides the fundamental metrics to quantify energy consumption and its associated greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. This data includes information on electricity usage, natural gas consumption, and waste management, which are critical to calculating a corporation’s total emissions:
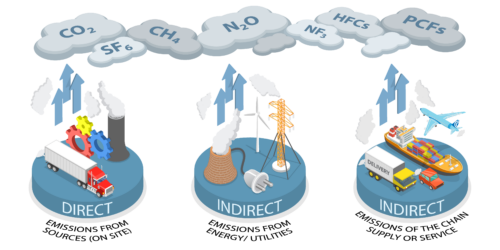
Knowing the exact amount of electricity used allows the corporation to apply specific emission factors, which convert electricity usage into equivalent CO2 emissions inventory for scope 2 according to the GHG protocol.
Equally significant is the data on natural gas consumption. Natural gas is a common fuel source for heating and industrial processes, and its combustion releases CO2 and other greenhouse gases. Accurate data on natural gas usage is crucial as it enables the corporation to calculate these emissions and account for them as inventory for their scope 1 according to the GHG protocol.
Waste management data is vital because different types of waste have varying impacts on the environment. For instance, biodegradable waste generates methane, a potent greenhouse gas, when it decomposes anaerobically in landfills. By understanding the quantity and types of waste produced, corporations can apply emission factors to determine the emissions as inventory for scope 3.4 according to the GHG protocol.
Chasing down the data
The primary business challenge lies in collecting data from various utilities for each facility the corporation operates. Several factors complicate this process. For instance, in the case of electricity usage, the corporation must gather consumption data from numerous suppliers across different regions, each of which may have different data formats and reporting frequencies. Moreover, accessing real-time data can be particularly challenging in areas with less advanced infrastructure.
The challenges for natural gas consumption are similar. The corporation needs to obtain data from multiple suppliers, each using different measurement units and conversion factors and often having inconsistent billing cycles.
Tracking waste management data adds another layer of complexity. This involves coordinating with numerous waste management services and differentiating between types of waste, such as recyclable and hazardous materials. Ensuring accurate reporting of waste quantities is also challenging. It requires corporations to navigate a fragmented landscape of utility providers, each with its own data reporting methods and schedules, making collecting consistent and comprehensive utility data a significant challenge.
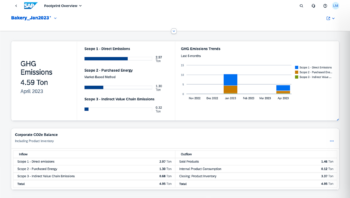
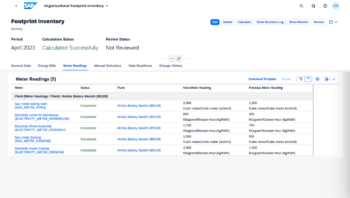
By mapping energy consumption directly to meters at production facilities, you can accurately report on carbon footprint and better detect opportunities to reduce GHG emissions. Above, utility data integrated into SAP Sustainability Footprint Management shows the overall corporate carbon footprint with a drill-down into the source CO2 contributors.
Automating data collection and carbon footprint calculation
Because this data collection and analysis process is so complex, it is, in most cases, a manual process. Someone has to download several invoices from different utility providers every month, extract the information from the digital invoices, and type it into a standardized spreadsheet or directly into carbon calculation software. Manual processes are always error-prone, ranging from missing items to misunderstanding the information on the invoices to typos during the manual transformation.
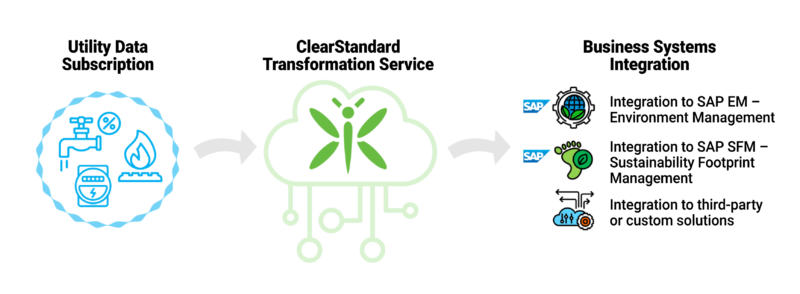
ClearStandard solves the data dilemma by hooking your business systems up to data feeds directly from your utility accounts. Moreover, you can improve the specificity of your reporting because ClearStandard lets you map meters to production lines for more accurate and timely consumption data which in turn provides more precise carbon footprint calculations.
Is ClearStandard right for you?
With thousands of utility accounts available for streaming electric, natural gas, and water usage data, it’s likely ClearStandard has you covered. Go ahead and search our database of providers or contact us for demo.